ABSTRACT
This article is based on a laboratory testing and aims to describe the latency difference between the wireless communication link and cable link on a autonomous unmanned ground vehicles with ZED VR camera. And figure out if the wireless link is high reliable for ensuring the 3D visual perception of a UGV.
1.Introduction
UGV is widely used in a variety of terrain difficult to reach or dangerous for human safety, eg for the location of a natural disaster, radiation, or to defuse the bomb in the military. In tele-operated search and rescue UGV, the 3D visual perception of the UGV environment has a deep impact on human-robot-interaction awareness of the UGV environment. Which requires
A highly real-time synchronization of state information, real-time feedback of gesture, action information and synchronous feedback of remote robot video. With there real time information the UGV can be precisely and wirelessly control in long range and non-line-of-sight environments.
These information data include both short data packets and real-time streaming media data, which are mixed together and transmitted to the control platform through the transmission link. Obviously, there are very high requirements on the delay of the wireless link.
1.1.Wireless communication link
IWAVE wireless communication link FDM-6600 Radio Module offers secure IP networking with end-to-end encryption and seamless Layer 2 connectivity, the FDM-6600 module can be easily integrated into almost any platform or application.
It's lightweight and small dimension are ideal for SWaP-C (Size, Weight,Power and Cost)- UAVs and unmanned ground vehicles in UHF, S-Band and C-Band frequency. It provides secure, highly reliable connectivity for real-time video transmission for mobile surveillance, NLOS (non-line-of-sight) communications, and command and control of drones and robotics.
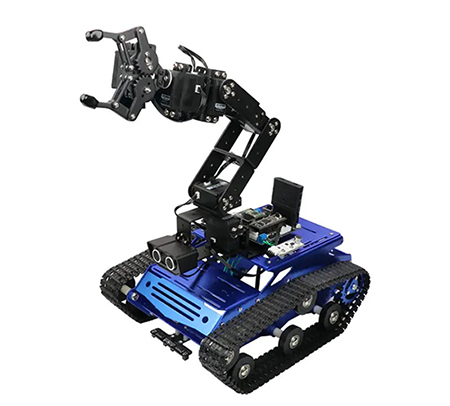

1.2.Unmanned ground vehicles
The robot is multi-terrain capable and can climb obstacles. It connects with a ZED camera for capturing video feed around the UGV. And the UGV use the FDM-6600 wireless link to receive video feeds from ZED on-board cameras. Simultaneously video feeds are sent to the operator station computer for generating the VR scenes from video data obtained by robot.
2.Test Content:
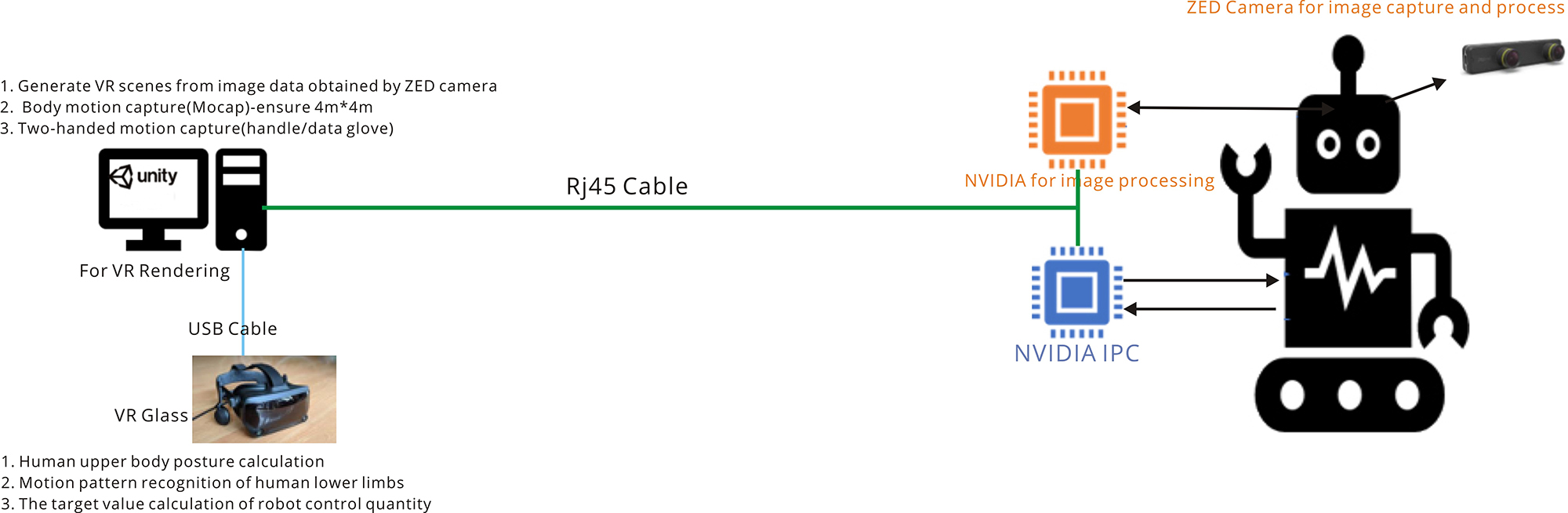
Testing the delay difference between IWAVE wireless transmission and RJ45 cable transmission when transmitting ZED Camera 720P*30FS video from the robot to the back-end VR server.
Firstly use IWAVE wireless link to transmit the video streaming, control data and other sensor data from NVIDIA IPC.
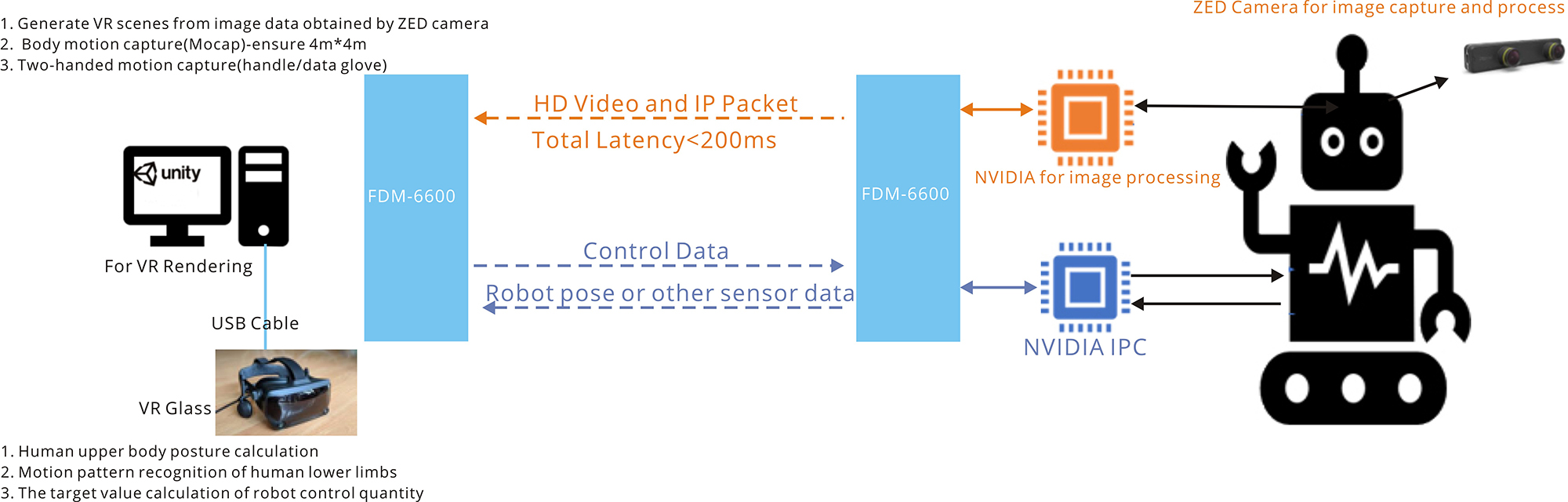
Secondly using a RJ45 cable to replace the wireless link for transmitting the image data, control data and sensor data from robot side to controller side.
3. Test Methods
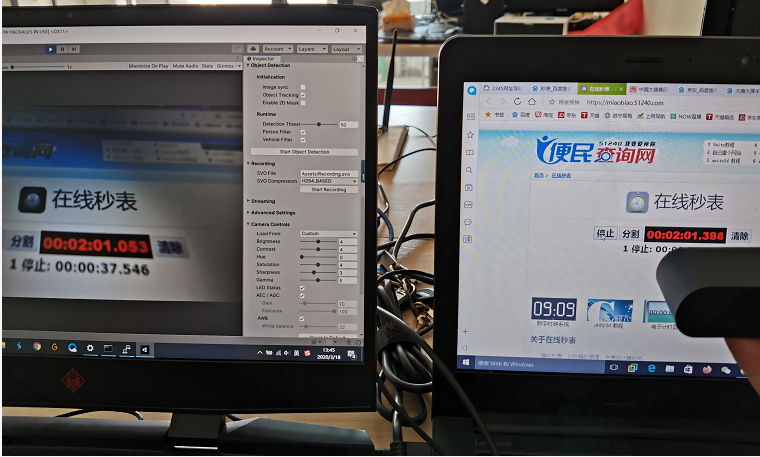
The ZED Camera of the robot shoots the stopwatch timing software, and then puts the VR server and the stopwatch software on the same screen to take the same photo (dual focus point) and record the difference between the two time points of the same photo.
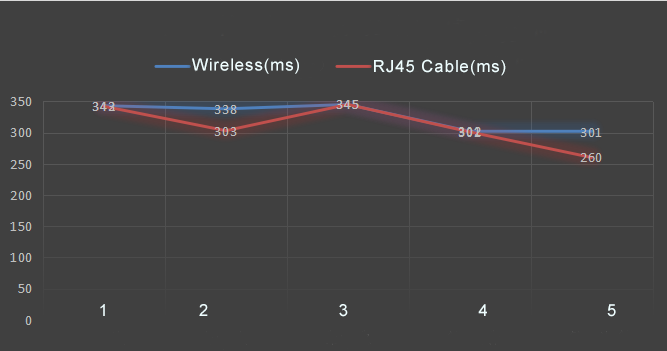
4.Test Results and Analysis:
|
Latency Data |
||||||
|
Times |
Timing Software | VR Sever Screen | IWAVE Wireless Communication Latency | Timing Software | VR Sever Screen | RJ45 Cable Latency |
| 1 | 7.202 | 7.545 | 343 | 7.249 | 7.591 | 342 |
| 2 | 4.239 | 4.577 | 338 | 24.923 | 25.226 | 303 |
| 3 | 1.053 | 1.398 | 345 | 19.507 | 19.852 | 345 |
| 4 | 7.613 | 7.915 | 302 | 16.627 | 16.928 | 301 |
| 5 | 1.598 | 1.899 | 301 | 10.734 | 10.994 | 260 |
|
||||||
5.Conclusions:
In this scenario, there is no significant difference between the latency of wireless communication for high-definition video acquisition, transmission, decoding, and display, and the latency of direct transmission via a network cable.
Post time: Feb-27-2023