As the digital age continues to progress, the need for faster and more reliable network speeds is paramount. Carrier aggregation (CA) has emerged as a key technology in meeting these demands, especially in the realm of 5G networks. In this blog, we'll delve into the basics of carrier aggregation, its classifications, functionalities, and applications.
What is Carrier Aggregation?
Carrier aggregation is a technology that allows multiple carriers, or spectrum resources, to be combined into a single, wider bandwidth channel. This technology effectively multiplies the available bandwidth, leading to increased network speed and capacity. In 4G LTE networks, carrier aggregation was introduced as a means to enhance performance, and it has since evolved significantly to power the blazing fast speeds of 5G.
Classifications of Carrier Aggregation
Carrier aggregation can be classified based on several factors, including the number of carriers aggregated, the frequency bands used, and the network architecture. Here are some common classifications:
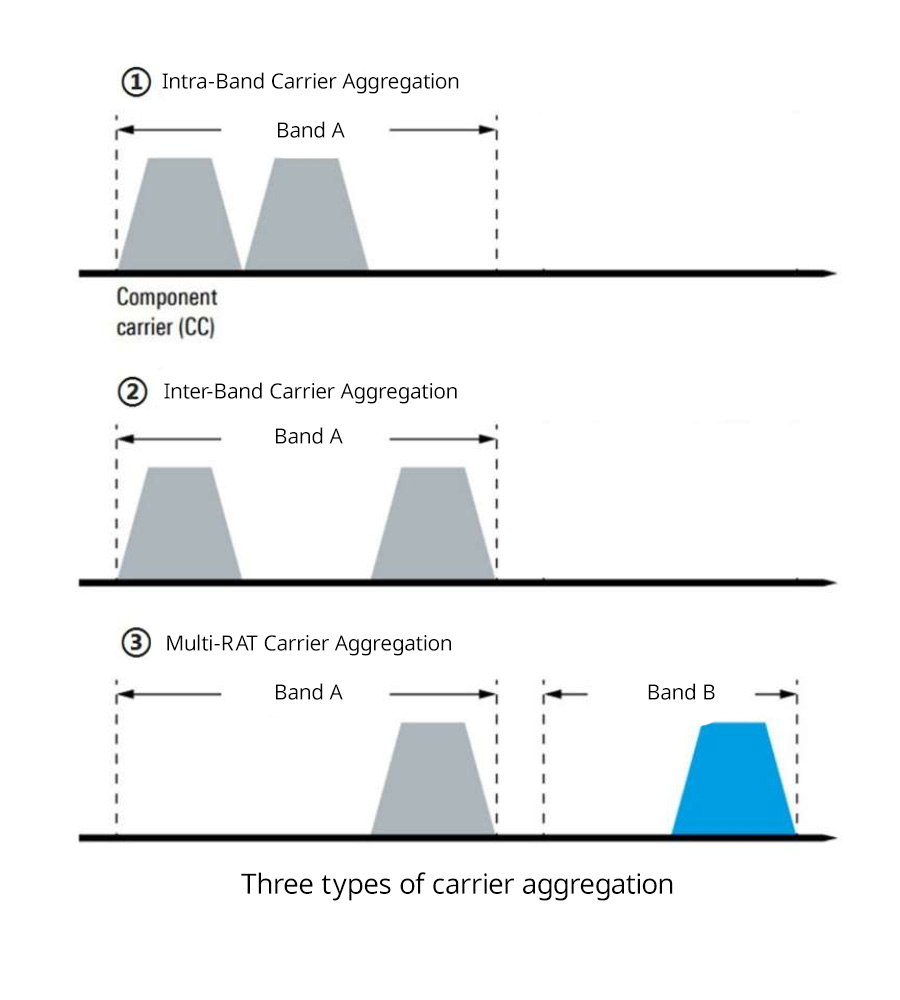
Intra-Band Carrier Aggregation
This type of carrier aggregation involves combining carriers within the same frequency band. It is typically used to enhance performance within a specific spectrum allocation.
Inter-Band Carrier Aggregation
Inter-band carrier aggregation combines carriers from different frequency bands. This allows operators to utilize fragmented spectrum allocations more efficiently, enhancing overall network capacity.
Multi-RAT Carrier Aggregation
Multi-RAT carrier aggregation goes beyond traditional cellular networks, combining carriers from different radio access technologies (RATs), such as 4G and 5G, to deliver a seamless user experience.
Advantages of Carrier Aggregation
Carrier aggregation offers several key functionalities that enable the high-speed capabilities of 5G networks:
- Increased Bandwidth: By combining multiple carriers, carrier aggregation significantly increases the overall bandwidth available to users. This translates into faster data speeds and a more responsive network.
Enhanced Spectral Efficiency: Carrier aggregation allows operators to utilize fragmented spectrum allocations more efficiently. By combining carriers from different bands or RATs, operators can maximize their spectrum utilization.
Flexible Resource Allocation: Carrier aggregation provides operators with greater flexibility in resource allocation. Depending on network conditions and user demand, carriers can be dynamically assigned to optimize network performance.
Applications of Carrier Aggregation
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): eMBB is a key use case of 5G networks, and carrier aggregation is instrumental in delivering the ultra-high speeds required for immersive experiences like 4K/8K video streaming and virtual reality.
Carrier aggregation plays a crucial role in enabling the various applications and use cases of 5G networks
Flexible Resource Allocation: Carrier aggregation provides operators with greater flexibility in resource allocation. Depending on network conditions and user demand, carriers can be dynamically assigned to optimize network performance.
In conclusion, carrier aggregation is a powerful technology that enables the high-speed capabilities of 5G networks. By combining multiple carriers into a wider bandwidth channel, carrier aggregation increases network speed, capacity, and spectral efficiency. As we continue to explore the possibilities of 5G and beyond, carrier aggregation will remain a crucial component in delivering the best user experience and supporting next-generation applications.
Ultra-High-Speed Internet: With increased bandwidth, carrier aggregation enables ultra-high-speed internet connections, enabling seamless streaming, online gaming, and cloud-based services.
Post time: May-31-2024



